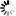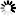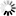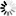Syntax:
integer_variable = sin( integer_variable ) integer_variable = cos( integer_variable ) integer_variable = tan( integer_variable )
Explanation:
GCBASIC supports Three Primary Trigonometric Functions
GCBASIC supports the following functions, sin(x), cos(x), tan(x), where x is a signed integer representing an angle measured in a whole number of degrees. The output values are also integers, represented as fixed point decimal fractions.
Details:
The sine, cosine and tangent functions are available for your programs simply by including the header file offering the precision you need.
#INCLUDE <TRIG2PLACES.H> gives two decimal places
#INCLUDE <TRIG3PLACES.H> gives three decimal places
#INCLUDE <TRIG4PLACES.H> gives four decimal placesIn fixed point representation, the decimal point is assumed. For example, with two places of accuracy, sin(60) returns 87, which you would interpret as 0.87. With three places, 866 is returned, to be interpreted as 0.866, and so on. Another way of thinking of this is to consider the two-place values as scaled up by 100, the three-place values scaled up by 1000 and the four-place values scaled up by 10,000.
Sine and Cosine are always defined, but remember that tangent fails to exist at 90 degrees, 270 degrees and all their coterminal angles. It is the responsibility of the calling program to avoid these special values.
Note that the tangent function is not available to four decimal places, since its value grows so rapidly, exceeding what the Integer data type can represent.
These routines are completely general. The input argument may be positive, negative or zero, with no restriction on the size. Further observe that lookup tables are used, so the routines are very fast, efficient and accurate.
Example: Show the trigonometric values to three decimal places.
;----- Configuration
#CHIP 16F88, 8 ;PIC16F88 RUNNING AT 8 MHZ
#CONFIG MCLR=OFF ;RESET HANDLED INTERNALLY
#INCLUDE <TRIG3PLACES.H>
;----- Constants
#define LCD_IO 4 ;4-bit mode
#define LCD_WIDTH 20 ;specified lcd width for clarity only. 20 is the default width
#define LCD_RS PortB.2 ;pin 8 is LCD Register Select
#define LCD_Enable PortB.3 ;pin 9 is LCD Enable
#define LCD_DB4 PortB.4 ;DB4 on pin 10
#define LCD_DB5 PortB.5 ;DB5 on pin 11
#define LCD_DB6 PortB.6 ;DB6a on pin 12
#define LCD_DB7 PortB.7 ;DB7 on pin 13
#define LCD_NO_RW 1 ;ground the RW line on LCD
;----- Variables
dim ii as integer
dim outStr, valStr as string
;----- Program
dir PortB out ;all outputs to the LCD
for ii = -720 to 720 ;arguments from -720 to 720
cls
print "sin(" ;print the label
print ii ;and the argument
print ")=" ;and closing parenthesis
locate 1,0
printTrig(sin(ii)) ;print value of the sine
wait 500 mS ;pause to view
cls ;do likewise for cosine
print "cos("
print ii
print ")="
locate 1,0
printTrig(cos(ii))
wait 500 mS ;pause to view
cls ;do likewise for tangent
print "tan("
print ii
print ")="
locate 1,0
printTrig(tan(ii))
wait 500 mS ;pause to view
next i
sub printTrig(in value as integer)
;print decently formatted trig results
outStr = "" ;assume positive (no sign)
if value < 0 then ;handle negatives
outStr = "-" ;prefix a minus sign
value = -1 * value ;but work with positives
end if
valStr = str(value)
length = len(valStr)
select case length
case 1:
outStr = outStr + "0.00" + valStr
case 2:
outStr = outStr + "0.0" + valStr
case 3:
outStr = outStr + "0." + valStr
case 4:
outStr = outStr + left(valStr,1) + "." + right(valStr,3)
case 5:
outStr = outStr + left(valStr,2) + "." + right(valStr,3)
end select
print outStr
end sub