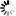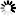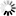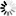Syntax:
The SPI interface allows for the transmission and receiption of data simultaneously on two lines (MOSI and MISO).
The Clock polarity (CPOL) and clock phase (CPHA) are the main parameters that define a clock format to be used by the SPI bus. Depending on CPOL parameter, SPI clock may be inverted or non-inverted. CPHA parameter is used to shift the sampling phase. If CPHA=0 the data are sampled on the leading (first) clock edge. If CPHA=1 the data are sampled on the trailing (second) clock edge, regardless of whether that clock edge is rising or falling.
CPOL=0, CPHA=0
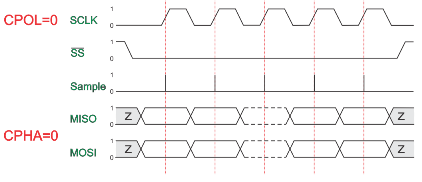
The data must be available before the first clock signal rising. The clock idle state is zero. The data on MISO and MOSI lines must be stable while the clock is high and can be changed when the clock is low. The data is captured on the clock’s low-to-high transition and propagated on high-to-low clock transition.
CPOL=0, CPHA=1
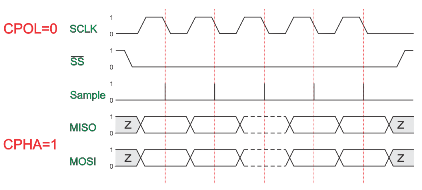
The first clock signal rising can be used to prepare the data. The clock idle state is zero. The data on MISO and MOSI lines must be stable while the clock is low and can be changed when the clock is high. The data is captured on the clock’s high-to-low transition and propagated on low-to-high clock transition.
CPOL=1, CPHA=0
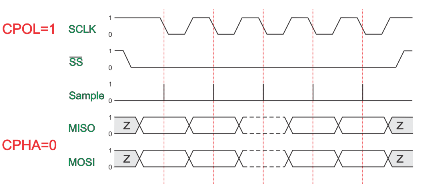
The data must be available before the first clock signal falling. The clock idle state is one. The data on MISO and MOSI lines must be stable while the clock is low and can be changed when the clock is high. The data is captured on the clock’s high-to-low transition and propagated on low-to-high clock transition.
CPOL=1, CPHA=1
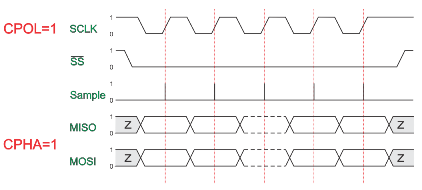
The first clock signal falling can be used to prepare the data. The clock idle state is one. The data on MISO and MOSI lines must be stable while the clock is high and can be changed when the clock is low. The data is captured on the clock’s low-to-high transition and propagated on high-to-low clock transition.
Key Commands
// Set the mode
SPIMode ( _Mode_ [, SPIClockMode]) //Legacy SPI
SPIMode ( _Mode_ , SPIClockMode) //18FxxQxx, 18FxxK42 and 18xxFK83 microcontrollers
// Send bytge and receive data byte
SPITransfer ( _OutByte_, _InByte_ )
// Send data byte
FastHWSPITransfer( _OutByte_ )
// USe MASTERSLOW | MASTER | MASTERFAST | MASTERULTRAFAST for specific AVRs only | MasterSSPADDMode for specific PICs SSPADD support
// The system constant `HWSPIMode` defaults to MASTERFAST when microcontroller frequency less or equal to 32 mhz
// Defaults to MASTER when microcontroller frequency more than 32 mhz.
// To change use the following method
#define HWSPIMode MASTERULTRAFASTThe GCBASIC used the microcontrollers hardware module for SPI. The example below shows an implementation of Hardware and Software SPI. Software SPI allows for a greater choice of ports to be used to control the SPI operations.
To use a second SPI hardware module use the suffix 2, as follows:
// Set the mode
SPIMode2 ( _Mode_ [, SPIClockMode]) //Legacy SPI
SPIMode2 ( _Mode_ , SPIClockMode) //18FxxQxx, 18FxxK42 and 18xxFK83 microcontrollers
// Send bytge and receive data byte
SPITransfer2 ( _OutByte_, _InByte_ )
// Send data byte
FastHWSPITransfer2( _OutByte_ )Example
This example demonstrates the SPI capabilities for the mega328p. The process is similar of any microcontroller..
This example show using the hardware SPI option and a sofware SPI option.
Using hardware SPI mode - make sure the #define SPI_HardwareSPI is not commented out.
Using software SPI mode - comment out #define SPI_HardwareSPI. The example code will then use software SPI.
Using multiple SPI devices
There will be use cases were you need to use more than one SPI target device at a time. In such cases the device defined for SPI must be inserted in your program for each device.
As an example using e-Paper and SRAM at the same time, with an hardware SPI would require #define SPISRAM_HARDWARESPI and #define EPD_HardwareSPI.
Obviously, when all SPI devices use the same SPI lines, you must select one device at a time by setting SPI Chip Select line
to OFF for the specific target SPI device, and you must set ON the SPI Chip Select line for any other SPI device - this is a normal convention of SPI usage. This is not specific to
GCBASIC..
Code overview
For more code examples see the demonstrations and the SPIMODE Help page.
In this example InitSPIMode calls SPIMode. If needed, when hardware mode, and set the port directions.
The sub SendByteviaSPI is called to handle whether to call the Hardware or use Software (bit-banging) SPI.
#chip mega328p, 16
#option explicit
#include <UNO_mega328p.h >
#define SPI_HardwareSPI 'comment this out to make into Software SPI but, you may have to change clock lines
'Pin mappings for SPI - this SPI driver supports Hardware SPI
#define SPI_DC DIGITAL_8 ' Data command line
#define SPI_CS DIGITAL_4 ' Chip select line
#define SPI_RESET DIGITAL_9 ' Reset line
#define SPI_DI DIGITAL_12 ' Data in | MISO
#define SPI_DO DIGITAL_11 ' Data out | MOSI
#define SPI_SCK DIGITAL_13 ' Clock Line
dir SPI_DC out
dir SPI_CS out
dir SPI_RESET out
dir SPI_DO Out
dir SPI_DI In
dir SPI_SCK Out
'If DIGITAL_10 is NOT used as the SPI_CS (sometimes called SS) the port must and output or set as input/pulled high with a 10k resistor.
'As follows:
'If CS is configured as an input, it must be held high to ensure Master SPI operation.
'If the CS pin is driven low by peripheral circuitry when the SPI is configured as a Master with the SS pin defined as an input, the
'SPI system interprets this as another master selecting the SPI as a slave and starting to send data to it!
'If CS is an output SPI communications will commence with no flow control.
dir DIGITAL_10 Out
DIM byte1 As byte
DIM byte2 As byte
DIM byte3 As byte
byte1 = 100 ' temp values (will come from potentiometer later)
byte2 = 150
byte3 = 200
InitSPIMode
do forever
set SPI_CS OFF;
set SPI_DC OFF;
SendByteviaSPI (byte1)
set SPI_CS ON;
set SPI_DC ON
set SPI_CS OFF;
set SPI_DC OFF;
SendByteviaSPI (byte2)
set SPI_CS ON;
set SPI_DC ON
set SPI_CS OFF;
set SPI_DC OFF;
SendByteviaSPI (byte3)
set SPI_CS ON;
set SPI_DC ON
wait 10 ms
loop
sub InitSPIMode
#ifdef SPI_HardwareSPI
SPIMode ( MasterFast, SPI_CPOL_0 + SPI_CPHA_0 )
#endif
set SPI_DO OFF;
set SPI_CS ON; therefore CPOL=0
set SPI_DC ON; deselect
End sub
sub SendByteviaSPI( in SPISendByte as byte )
set SPI_CS OFF
set SPI_DC OFF;
#ifdef SPI_HardwareSPI
FastHWSPITransfer SPISendByte
set SPI_CS ON;
exit sub
#endif
#ifndef SPI_HardwareSPI
repeat 8
if SPISendByte.7 = ON then
set SPI_DO ON;
else
set SPI_DO OFF;
end if
SET SPI_SCK On; ; therefore CPOL=0 ==ON, and, where CPOL=1==ON
rotate SPISendByte left
set SPI_SCK Off; ; therefore CPOL=0 =OFF, and, where CPOL=1==OFF
end repeat
set SPI_CS ON;
set SPI_DO OFF;
#endif
end SubSee also SPIMode,SPITransfer,FastHWSPITransfer